From Chaos to Clarity: Mastering Data Governance
The Infodemic: Navigating the Challenges in Entering the Age of AI
The current digital age is characterized by an overabundance of data. The rapid evolution of technology, the plummeting costs of hardware and the ubiquity of cloud services have all contributed to the proliferation of data generation and processing.
However, as the volume of data expands, so does the complexity of managing it. The increasing utilization of non-traditional data sources adds another layer of challenge to data stewardship.
This presents the industry with a significant question: How can organizations navigate the future of AI when the pool of raw data is vast and ever-growing?
The answer may not lie in the mere accumulation of more data, but in its effective governance. In this context, data governance emerges not merely as an option, but as an essential asset — a strategic solution to a tangible challenge. Effective data governance is crucial for the policing of AI solutions, ensuring that they are used ethically and responsibly.
A Framework for Efficiency
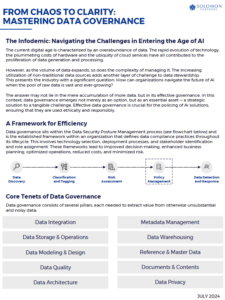
Data governance sits within the Data Security Posture Management process (see flowchart in PDF) and is the established framework within an organization that defines data compliance practices throughout its lifecycle. This involves technology selection, deployment processes, and stakeholder identification and role assignment. These frameworks lead to improved decision-making, enhanced business planning, optimized operations, reduced costs, and minimized risk.
Core Tenets of Data Governance
Data governance consists of several pillars, each needed to extract value from otherwise unsubstantial and noisy data:
- Data Integration
- Metadata Management
- Data Storage & Operations
- Data Warehousing
- Data Modeling & Design
- Reference & Master Data
- Data Quality
- Documents & Contents
- Data Architecture
- Data Privacy
Need for Governance
As the demand for high-quality data intensifies across various sectors, including financial services, the significance of data governance continues to gain recognition. The implementation of data governance tools enhances data usability, availability, quality, security, and lineage. With the escalating complexity of data, the necessity for third-party software tools, sometimes referred to as Data Governance as a Service, has become increasingly evident.
Benefits to Adapting Data Governance as a Service (DGaaS)
DGaaS is a cloud-based strategy that utilizes cloud infrastructure to equip organizations with the essential tools, processes, and expertise required for effective data governance. Pivotal applications are:
METADATA MANAGEMENT
DGaaS platforms offer a centralized data catalog that provides comprehensive information about the organization’s data assets, enabling users to understand the context and usage of data
QUALITY MANAGEMENT
Solutions include tools to assess and improve data quality, track issues and implement measures to ensure data accuracy and consistency
ACCESS CONTROL AND PRIVACY MANAGEMENT
Allow organizations to define access controls, permissions and authentication mechanisms for secure accessibility, collaboration and compliance with regulations
COMPLIANCE AND REGULATORY MANAGEMENT
Enforce data governance policies and comply with regulations by configuring rules and alerts within the DGaaS platform
Outlook
The rapid growth of AI tools is transforming data governance and management, with increasing adoption of AI and ML automation solutions. These advancements are set to guide and execute end-to-end data governance policies and standards in organizations, reducing human intervention during compliance. Concurrently, DGaaS is emerging as a flexible and efficient approach for organizations to establish and maintain data governance practices. As the data landscape evolves, DGaaS offers a critical, scalable solution for effective governance without the need for in-house infrastructure. This dual approach of AI-driven automation and DGaaS is shaping the future of data governance.